Understanding the optimal temperature range for your CPU is crucial for maintaining performance and longevity.
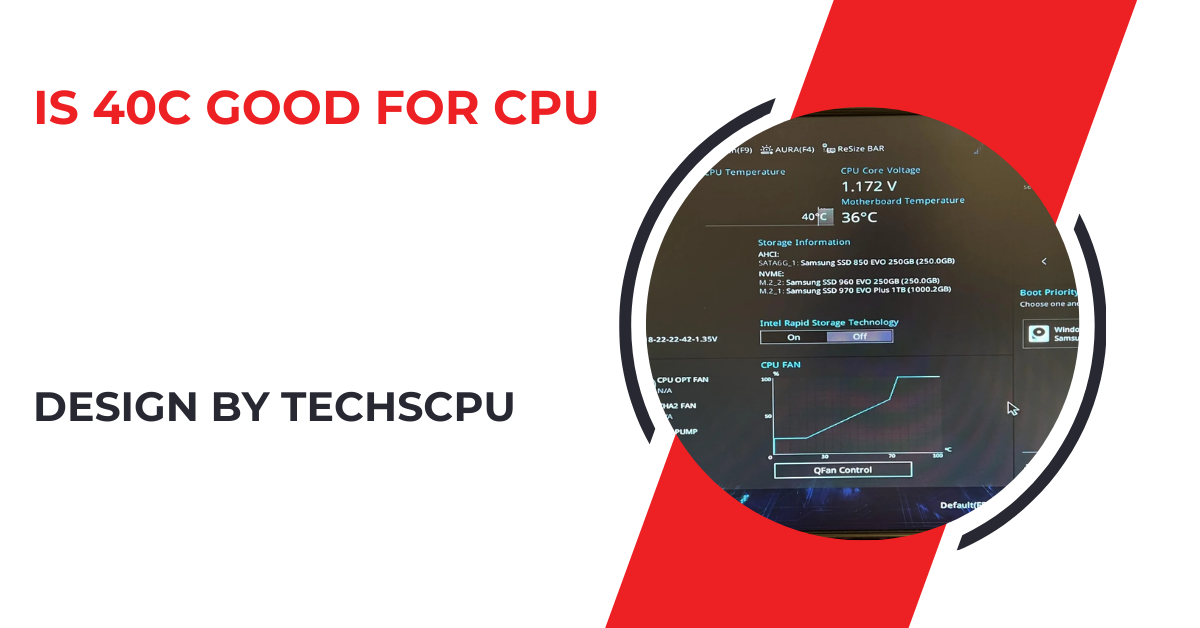
A CPU temperature of 40°C is generally considered good, indicating effective cooling and safe operation. Proper cooling practices and regular monitoring can help maintain optimal performance and extend your CPU’s lifespan.
In this article, we’ll explore whether a CPU temperature of 40°C is considered good, what factors influence CPU temperature, and how to manage and monitor it effectively.
What is the Ideal CPU Temperature?
The ideal CPU temperature can vary depending on the specific processor and its usage. However, most CPUs are designed to operate efficiently within a certain temperature range.
For many modern CPUs, idle temperatures between 30°C and 40°C are considered normal and safe. Under load, temperatures can rise significantly, but staying below 85°C is typically recommended to avoid thermal throttling and potential damage.
Safe Temperature Ranges:
- Idle Temperature: When your system is not under significant load, an idle CPU temperature between 30°C and 40°C is generally considered safe and normal.
- Load Temperature: During intensive tasks like gaming, video editing, or benchmarking, CPU temperatures can rise to 70°C to 85°C. While this is higher, it’s still within safe limits for most CPUs.
- Critical Temperature: Exceeding 90°C can lead to thermal throttling, reduced performance, and potential long-term damage to the CPU. It’s crucial to avoid sustained high temperatures.
Is 40°C a Good Temperature for Your CPU?
A CPU temperature of 40°C is generally considered good, especially when the system is idle or under light load. This temperature indicates that your cooling solution is effectively managing the heat generated by the CPU. It provides a buffer for temperature increases under heavier loads, ensuring that the CPU remains within safe operating limits.
Benefits of a Cooler CPU:
- Enhanced Performance: Lower temperatures can help maintain higher clock speeds and overall system performance.
- Longevity: Consistently lower temperatures reduce wear and tear on the CPU, extending its lifespan.
- Stability: A cooler CPU is less likely to experience thermal throttling or instability during intensive tasks.
Factors Influencing CPU Temperature:
Several factors can affect your CPU’s temperature:
- Ambient Temperature: The temperature of the environment where your computer is located can impact CPU temperature. Cooler room temperatures help maintain lower CPU temperatures.
- Cooling Solution: The type and quality of your CPU cooler, whether it’s an air cooler, liquid cooler, or stock cooler, significantly affect how well your CPU’s temperature is managed.
- Thermal Paste: Proper application of thermal paste between the CPU and cooler can enhance heat transfer and improve cooling efficiency.
- Case Airflow: Good case ventilation and airflow help dissipate heat more effectively, lowering the overall system temperature.
- Workload: The type of tasks your CPU is handling can cause temperatures to vary. Intensive tasks like gaming, video editing, or rendering will generate more heat compared to browsing the web or running simple applications.
- Overclocking: Running your CPU at higher speeds than its base frequency can significantly increase temperature. Effective cooling solutions are essential to manage this extra heat.
Also Read: How to Remove Thermal Paste from Cpu Pins – Step-by-Step Guide!
How to Monitor CPU Temperature:
Monitoring your CPU temperature is essential to ensure it stays within safe limits. Here are some tools and methods to help you keep an eye on your CPU temperature:
- BIOS/UEFI: Most motherboards allow you to check the CPU temperature directly in the BIOS or UEFI settings. This is useful for a quick check when booting up your computer.
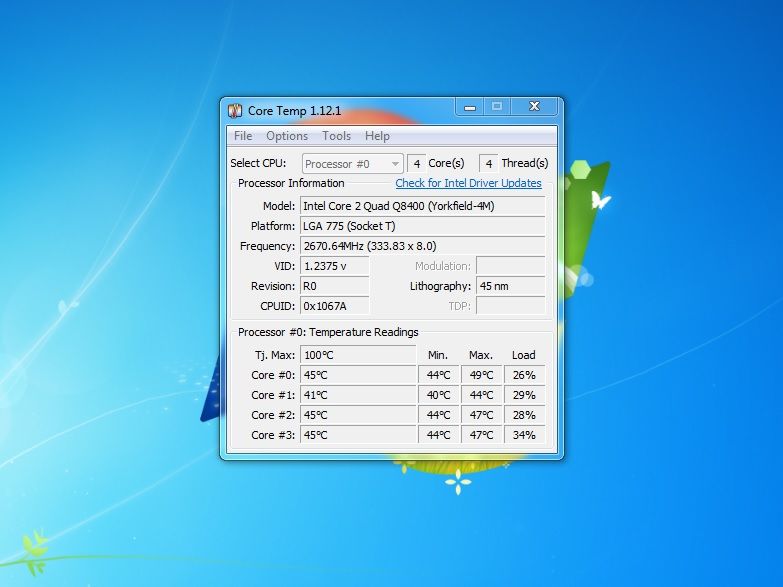
- Software Tools: Various software programs like HWMonitor, Core Temp, and Real Temp can provide real-time temperature readings and detailed thermal information.
- Manufacturer Tools: Some CPU manufacturers offer their own monitoring tools, such as Intel’s Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU) or AMD’s Ryzen Master, which are optimized for their processors.
- System Monitoring Suites: Comprehensive monitoring tools like AIDA64 and HWiNFO64 offer detailed insights into various system components, including CPU temperature.
Tips for Maintaining Optimal CPU Temperature:
- Improve Cooling: Invest in a high-quality CPU cooler or consider upgrading to a more efficient cooling solution if you notice high temperatures.
- Enhance Case Airflow: Ensure your PC case has good airflow by using additional case fans and keeping cables organized to avoid obstructing air paths.
- Regular Cleaning: Dust buildup can hinder cooling performance. Regularly clean your computer’s interior, including fans and heat sinks, to maintain optimal airflow.
- Thermal Paste Application: Reapply thermal paste every couple of years or if you notice increasing temperatures, ensuring a good thermal interface between the CPU and cooler.
- Monitor and Adjust: Keep an eye on CPU temperatures, especially under load, and adjust your cooling strategy as needed to maintain safe operating temperatures.
- Optimize Fan Curves: Use your motherboard’s BIOS or dedicated software to create custom fan curves that adjust fan speeds based on temperature readings for more efficient cooling.
Advanced Cooling Solutions:
For those looking to push their systems further, advanced cooling solutions can provide significant benefits:
- Liquid Cooling: All-in-one (AIO) liquid coolers or custom loop liquid cooling systems offer superior cooling performance compared to air coolers. They can maintain lower temperatures even under heavy loads.
- High-End Air Coolers: High-quality air coolers with larger heatsinks and multiple fans can effectively manage heat for powerful CPUs.
- Thermoelectric Coolers: These are specialized coolers that use the Peltier effect to provide extreme cooling, though they require careful installation and power management.
- Sub-Ambient Cooling: Techniques like phase change cooling or using liquid nitrogen (LN2) are used in extreme overclocking scenarios but are impractical for everyday use due to their complexity and cost.
FAQ’s
1. What is the ideal CPU temperature range?
The ideal CPU temperature range varies by processor, but typically, idle temperatures between 30°C and 40°C are safe, and load temperatures should stay below 85°C.
2. Is 40°C a good temperature for my CPU?
Yes, 40°C is a good temperature, indicating effective cooling, especially when the system is idle or under light load.
3. What factors affect CPU temperature?
Factors include ambient temperature, cooling solution, thermal paste application, case airflow, workload, and overclocking.
4. How can I monitor my CPU temperature?
You can monitor CPU temperature using BIOS/UEFI, software tools like HWMonitor and Core Temp, manufacturer tools like Intel’s XTU and AMD’s Ryzen Master, or comprehensive monitoring suites like AIDA64 and HWiNFO64.
5. Why is my CPU temperature high?
High CPU temperatures can be due to poor cooling solutions, inadequate case airflow, dust buildup, improper thermal paste application, or high ambient temperatures.
6. How can I lower my CPU temperature?
Improve your cooling solution, enhance case airflow, regularly clean your computer’s interior, reapply thermal paste, and optimize fan curves.
Conclusion
A CPU temperature of 40°C is considered good and indicates effective cooling, especially during idle or light workloads. By understanding the factors that influence CPU temperature and implementing proper cooling practices, you can maintain optimal performance and extend the lifespan of your CPU. Regular monitoring and maintenance are key to ensuring your system runs smoothly and efficiently.