Determining whether you need two CPU power cables depends on your CPU’s power requirements and your motherboard’s design. High-performance CPUs and overclocking setups typically benefit from dual power connectors for enhanced stability and performance.
This guide will help you determine if you need two CPU power cables and how to connect them correctly.
Understanding CPU Power Requirements:
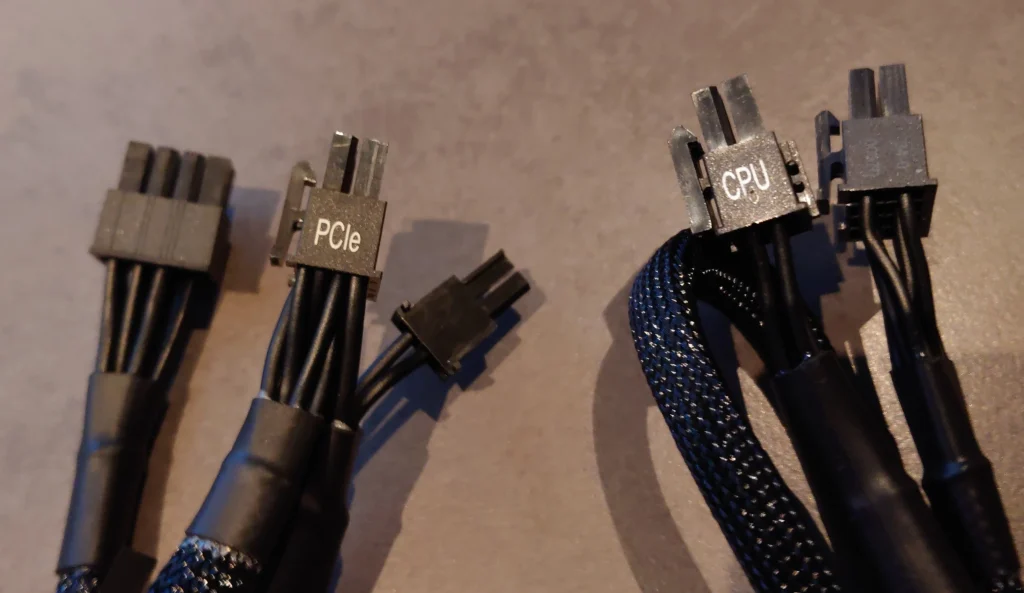

Modern CPUs, especially high-performance ones, require substantial power to operate efficiently. This power is delivered through the motherboard’s CPU power connectors, usually labeled as EPS12V connectors. These connectors are designed to provide the necessary voltage and current to the CPU.
Single vs. Dual CPU Power Connectors:
Single CPU Power Connector:
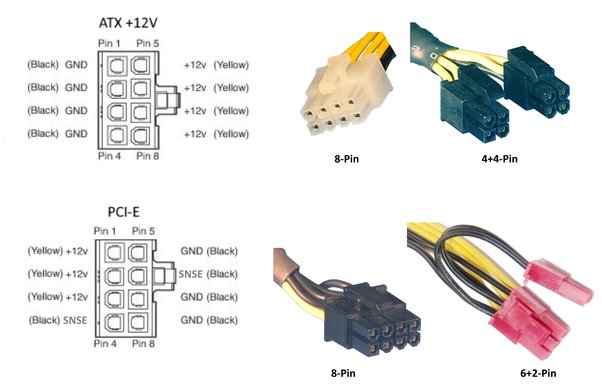
Most mid-range and entry-level motherboards and CPUs can operate efficiently with a single 8-pin (4+4) CPU power connector. This setup provides adequate power for standard use cases, including gaming and general productivity tasks.
- Usage: Suitable for most mainstream CPUs and motherboards.
- Power Delivery: Typically sufficient for CPUs with lower power consumption.
- Configuration: One 8-pin (4+4) connector from the power supply unit (PSU) to the motherboard.
Dual CPU Power Connectors:
High-end CPUs and motherboards, particularly those designed for overclocking or extreme performance, often feature two CPU power connectors (8-pin and 4-pin or two 8-pin connectors). This setup ensures that the CPU receives enough power, especially under heavy loads or when overclocking.
- Usage: Necessary for high-performance CPUs and overclocking.
- Power Delivery: Provides additional power stability and prevents power shortages.
- Configuration: Two connectors from the PSU, typically an 8-pin and an additional 4-pin or another 8-pin connector.
When Do You Need Two CPU Power Cables?
- High-Performance CPUs: If you have a high-end CPU like the Intel Core i9 or AMD Ryzen 9, which consumes more power, two CPU power cables may be required to ensure stable performance.
- Overclocking: When overclocking your CPU, additional power is needed to maintain stability and performance. Dual power connectors provide the extra power needed.
- Motherboard Requirements: Some motherboards, particularly those designed for gaming or professional workstations, come with two CPU power connectors to support high power consumption and improve stability.
Also Read: 1150 Socket Cpu List – Top Picks and Performance!
How to Connect Two CPU Power Cables:
If your motherboard and PSU support dual CPU power cables, follow these steps to connect them properly:
- Identify the Connectors: Locate the CPU power connectors on your motherboard. They are typically located near the CPU socket and labeled as EPS12V or CPU_PWR1 and CPU_PWR2.
- Connect the Cables: Plug the 8-pin (4+4) connector from your PSU into the primary CPU power socket on the motherboard. Then, connect the additional 4-pin or 8-pin connector into the secondary CPU power socket.
- Secure the Connections: Ensure that the connectors are firmly seated to prevent any power issues.
- Check the PSU Manual: Refer to your PSU manual for specific instructions on connecting CPU power cables, as some PSUs have dedicated ports for multiple CPU power connections.
Benefits of Using Two CPU Power Cables:
- Enhanced Stability: Using two CPU power cables can provide more stable power delivery, which is especially important for high-end CPUs and overclocking.
- Improved Performance: Adequate power supply can prevent throttling and ensure that your CPU runs at its full potential.
- Overclocking Headroom: With additional power available, you have more headroom for overclocking, allowing you to push your CPU further without compromising stability.
- Future-Proofing: If you plan to upgrade your CPU in the future, having a dual power setup can ensure compatibility with more power-hungry processors.
Potential Issues and Solutions:
- Insufficient Power Supply: Ensure your PSU has enough wattage and the necessary connectors to support dual CPU power cables. A high-quality PSU with a higher wattage rating is recommended for high-end systems.
- Cable Management: Proper cable management is crucial to maintain airflow and prevent overheating. Use cable ties and routing channels to keep the cables organized and out of the way.
- Compatibility Issues: Not all motherboards and PSUs are designed for dual CPU power connectors. Check the specifications of your components to ensure compatibility before attempting to connect two CPU power cables.
- Overloading the PSU: Distributing power across multiple rails can prevent overloading a single rail. Ensure that your PSU can handle the power distribution effectively.
Common Myths About CPU Power Cables:
- More Cables Always Mean Better Performance: While additional power cables can enhance stability and performance, they are not always necessary. The need for dual CPU power cables depends on your specific CPU and usage scenario.
- Any PSU Can Support Dual CPU Power Cables: Only high-quality PSUs designed with multiple CPU power connectors can effectively support dual power setups. Always check your PSU’s specifications.
- All Motherboards Require Two CPU Power Cables: Not all motherboards are designed to utilize two CPU power cables. Typically, only high-end or enthusiast motherboards have dual CPU power connectors.
FAQ’s
1. What is the purpose of CPU power cables?
CPU power cables deliver the necessary voltage and current from the PSU to the CPU for stable operation.
2. Can I use a single CPU power cable for all CPUs?
Most mid-range CPUs can operate with a single 8-pin power cable, but high-performance CPUs may require two.
3. Why do some motherboards have two CPU power connectors?
Dual connectors provide extra power stability and are often needed for overclocking or high-performance CPUs.
4. Is it necessary to connect both CPU power cables?
It depends on your CPU and motherboard specifications. For high-end setups, it’s often recommended to connect both.
5. Can using two CPU power cables improve performance?
Yes, using two cables can enhance stability and provide better power delivery, especially for overclocked systems.
6. What happens if I don’t connect both CPU power cables?
If your system requires both and you don’t connect them, it might lead to instability or failure to boot.
7. Are dual CPU power cables needed for gaming PCs?
They are usually needed for high-end gaming PCs with powerful CPUs that require more power.
8. How do I know if my PSU supports dual CPU power cables?
Check your PSU’s specifications to see if it has the necessary connectors for dual CPU power cables.
9. Can I use an adapter to add a second CPU power cable?
It’s better to use a PSU that naturally supports dual CPU power cables for reliability.
10. Is it difficult to connect two CPU power cables?
No, it’s straightforward. Just plug the connectors into the corresponding CPU power sockets on the motherboard.
Conclusion
Whether you need one or two CPU power cables depends on your CPU’s power requirements, motherboard design, and overclocking plans. Most mid-range systems are fine with a single 8-pin connector, but high-performance systems and overclocking setups benefit from two. Always check your motherboard and PSU specifications to ensure proper power delivery and system stability.