CPU drivers are essential software that facilitate communication between the CPU and the operating system, ensuring optimal performance, stability, and compatibility. Regularly updating them is crucial to maintain system efficiency, security, and smooth operation.
In this guide, we will explore what CPU drivers are, why they are important, how to manage them, and address common issues related to them. This comprehensive article will provide you with everything you need to know about CPU drivers, whether you are a casual user or a tech enthusiast.
What Are CPU Drivers?
Understanding the Basics:
At its core, a CPU driver is a specialized software that enables communication between the CPU and the operating system. Without this driver, the OS would not know how to interact with the CPU, leading to performance issues, hardware malfunctions, or even complete system failure. Essentially, CPU drivers act as intermediaries that translate the OS’s commands into instructions that the CPU can execute.
Role of CPU Drivers in the System:
- Hardware Integration: Ensures that the CPU integrates seamlessly with other hardware components like the motherboard, RAM, graphics card, and storage devices.
- Resource Management: Helps allocate CPU resources efficiently, prioritizing tasks to maintain smooth system performance.
- Power Management: Optimizes power consumption by adjusting the CPU’s power states based on workload, thereby extending battery life on laptops and reducing heat output.
Types of CPU Drivers:
- Standard CPU Drivers: Pre-installed by the operating system and designed to work with a broad range of CPUs. These drivers offer basic functionality but may not support advanced features of specific CPUs.
- Manufacturer-Specific Drivers: Provided by CPU manufacturers like Intel or AMD, these drivers are tailored to the specific architecture and features of their processors, offering enhanced performance, stability, and compatibility.
- Chipset Drivers: Often bundled with CPU drivers, chipset drivers facilitate communication between the CPU and motherboard, optimizing the entire platform’s performance.
The Importance of Keeping CPU Drivers Updated:
Regularly updating your CPU drivers is critical for several reasons. While many users overlook this aspect of system maintenance, it can significantly impact your computer’s performance, security, and overall user experience.
Enhanced System Performance:
One of the primary reasons to update CPU drivers is to ensure that your system performs at its best. Manufacturers frequently release driver updates that include performance enhancements, enabling your CPU to handle more tasks simultaneously and reducing bottlenecks.
Improved Security:
In an age where cybersecurity threats are increasingly sophisticated, keeping your CPU drivers up-to-date is essential. Updated drivers often include security patches that protect against vulnerabilities, preventing unauthorized access to your system and safeguarding your data.
Also Read: Bad Cpu Type In Executable – A Detailed Overview!
Greater Software Compatibility:
As technology evolves, new software applications often require the latest drivers to function correctly. For instance, cutting-edge video editing software or high-end games may not run smoothly, or at all, if the CPU drivers are outdated. Ensuring compatibility with the latest software is a key reason to keep drivers current.
Bug Fixes and Error Corrections:
Driver updates are not just about adding new features; they also address existing bugs and errors that could cause system instability. For example, an update might resolve issues like unexpected crashes, freezes, or blue screens of death (BSOD).
Energy Efficiency:
Modern CPU drivers often include power management improvements, which can lead to better energy efficiency. This is particularly important for laptops, where battery life can be significantly extended by reducing unnecessary power consumption.
How to Check and Update CPU Drivers:
Knowing how to check and update your CPU drivers is an essential skill for any computer user. Whether you’re using a Windows, Mac, or Linux system, the process is straightforward but varies slightly depending on the platform.
Updating CPU Drivers on Windows:
Using Device Manager:
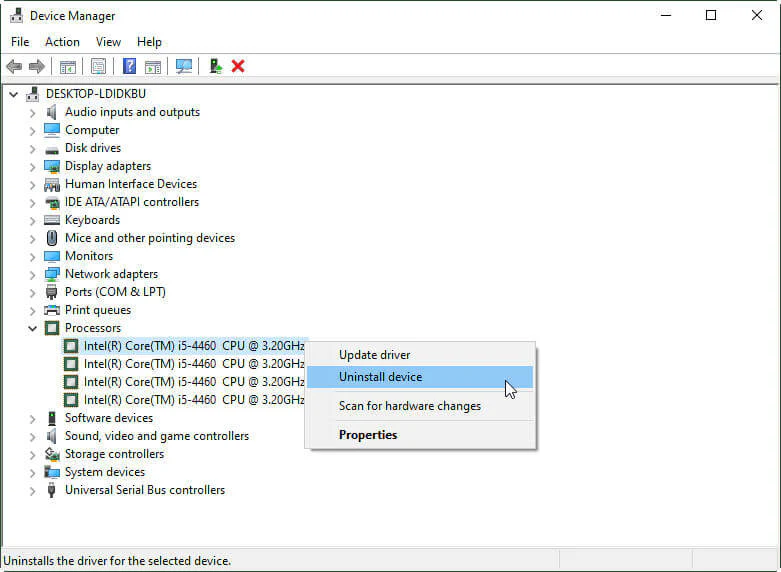
- Press Win + X and select Device Manager from the menu.
- In Device Manager, expand the Processors section.
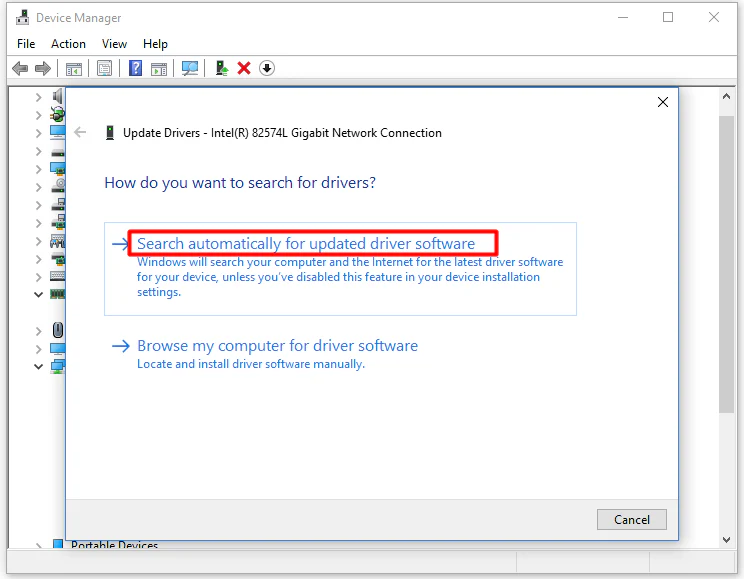
- Right-click on your CPU and select Update Driver.
- Choose the option to search automatically for updated driver software. Windows will search for the latest driver version and install it if available.
Windows Update:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update.
- Click on Check for updates. If a CPU driver update is available, it will be downloaded and installed automatically.
Manufacturer’s Website:
- Visit your CPU manufacturer’s website (e.g., Intel, AMD).
- Enter your CPU model number to find the latest drivers.
- Download and install the drivers manually following the provided instructions.
2. Updating CPU Drivers on macOS:
- macOS Updates: Apple does not provide separate driver updates; instead, CPU driver updates are included within macOS updates. To update, go to System Settings > Software Update and install any available updates.
3. Updating CPU Drivers on Linux:
- Using Terminal Commands: On Linux systems, CPU driver updates are typically handled through package managers or included in kernel updates. You can update your CPU drivers by updating the kernel using commands like sudo apt-get upgrade (for Debian-based systems) or sudo dnf update (for Fedora-based systems).
- Manual Installation: Advanced users can compile and install custom drivers from source if needed, though this is usually only necessary for specific hardware configurations or custom-built systems.
Troubleshooting Common CPU Driver Issues:
Despite the importance of CPU drivers, users often encounter issues that can lead to system instability, reduced performance, or even hardware failure. Below are some common problems and how to address them.
Driver Conflicts:
Conflicting drivers can arise when multiple drivers attempt to control the same hardware component. This often occurs when old drivers are not properly uninstalled before new ones are installed. To resolve this:
- Uninstall any outdated or unnecessary drivers through Device Manager before updating to the latest version.
- Use a third-party driver uninstaller tool to remove residual files that may cause conflicts.
System Crashes and Blue Screens:
Outdated, corrupted, or incompatible drivers are a common cause of system crashes and blue screens of death (BSOD). To troubleshoot:
- Boot your system into Safe Mode and roll back the CPU driver to a previous stable version.
- Use the built-in Windows Troubleshooter or third-party diagnostic tools to identify and resolve driver-related issues.
Slow System Performance:
Poor system performance can be a result of improperly installed drivers or outdated drivers that do not support newer software. Improving performance involves:
- Ensuring that all drivers are up-to-date and properly installed.
- Disabling unnecessary background processes or services that might be hogging CPU resources.
Compatibility Issues with New Hardware or Software:
New hardware or software may require updated drivers to function correctly. If you experience compatibility issues:
- Check for driver updates specifically released for the new hardware or software.
- Consider using beta drivers offered by manufacturers for cutting-edge hardware, though they may come with bugs.
Also Read: Why Is Mac Cpu Underperforming – A Complete Overview!
Advanced Tips for Managing CPU Drivers:
- Regular Backup of Drivers: Before making any updates, it’s wise to back up your existing drivers. This allows you to restore them if the update causes issues. Tools like DriverBackup! or Double Driver can automate this process.
- Use of Driver Management Software: For users who want to streamline the process, driver management software like Driver Booster or Snappy Driver Installer can automatically check for and install the latest drivers, saving time and ensuring that no driver is missed.
- Monitor System Performance: After updating CPU drivers, keep an eye on system performance using tools like Task Manager on Windows or Activity Monitor on macOS. Check for unusual CPU usage or temperature spikes, which might indicate a problem with the new driver.
- Understand Beta Drivers: Sometimes, manufacturers release beta versions of drivers for testing purposes. While these can offer performance boosts or new features, they may also introduce new bugs. Use beta drivers only if you are comfortable with potential instability.
FAQ’s
1. What is a CPU driver?
A CPU driver is software that enables communication between the CPU and the operating system, ensuring the CPU functions correctly and efficiently.
2. Why is it important to update CPU drivers?
Updating CPU drivers enhances system performance, security, and compatibility with new software, and fixes bugs that may cause system instability.
3. How do I update CPU drivers on Windows?
You can update CPU drivers via Device Manager, Windows Update, or by downloading the latest drivers directly from the CPU manufacturer’s website.
4. Can outdated CPU drivers cause system crashes?
Yes, outdated or incompatible CPU drivers can lead to system crashes, blue screens of death (BSOD), and reduced system performance.
5. How do I resolve driver conflicts?
To resolve driver conflicts, uninstall outdated drivers, use a driver uninstaller tool, and then install the latest drivers.
6. Are CPU drivers updated separately on macOS?
No, CPU driver updates on macOS are included in regular system updates via Software Update.
Conclusion
CPU drivers are crucial for seamless communication between your CPU and operating system, ensuring optimal performance, security, and compatibility. Regularly updating them is vital for maintaining system stability and efficiency. Whether you’re a casual user or an enthusiast, understanding and managing CPU drivers is key to a smooth and reliable computing experience.